# Python Scripting
This add-on provides support for Python 3 that can be used as a scripting language within automation rules. It is based on GraalPy (opens new window) from the GraalVM project (opens new window).
Also included is openhab-python (opens new window), a Python library to support automation in openHAB. It provides convenient access to common core openHAB functions that make the full range of Java APIs easily accessible and usable.
# Creating Python Scripts
When this add-on is installed, you can select Python 3 as a scripting language when creating a script action within the rule editor of the UI.
Alternatively, you can create scripts in the automation/python configuration directory.
If you create an empty file called test.py, you will see a log line with information similar to:
... [INFO ] [ort.loader.AbstractScriptFileWatcher] - (Re-)Loading script '/openhab/conf/automation/python/test.py'
Use the console logging (opens new window) commands to enable debug logging for the automation functionality:
log:set DEBUG org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting
# Rules
Let’s start with a simple script
from openhab import rule
from openhab.triggers import GenericCronTrigger
@rule( triggers = [ GenericCronTrigger("*/5 * * * * ?") ] )
class Test:
def execute(self, module, input):
self.logger.info("Rule was triggered")
# PY Transformation
Or as transformation inline script
String Test "Test [PY(|'String has ' + str(len(input)) + 'characters'):%s]"
# More Scripting
A complete Documentation about Python Scripting Rules and Transformation Scripts can be found at
>> openHAB Python Scripting << (opens new window)
including all examples above, much more detailed.
# Add-on Administration
# Configuration
Web based config dialog can be found via Web UI => Settings / Add-on Settings / Python Scripting
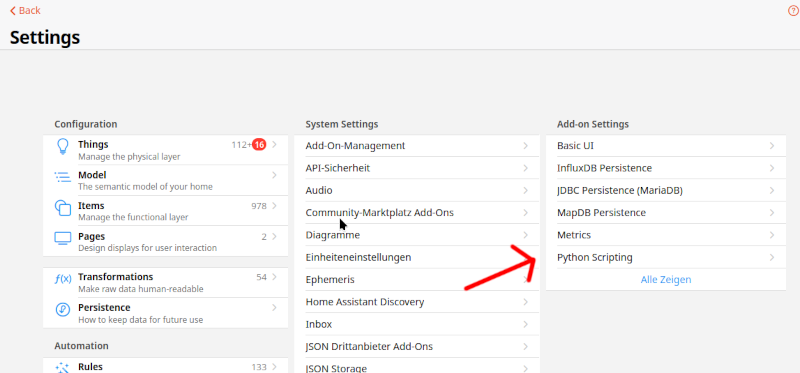
Additionally, you can configure the Add-on via a config file /openhab/services/pythonscripting.cfg like below.
Configuration note
If you use the marketplace version of this Add-on, it is necessary to use the config file. OpenHAB has a bug which prevents the web based config dialog to work correctly for kar file based Add-ons.
# Activate openHAB Python helper module and inject scope and helper objects into rules
#
# Install openHAB Python helper module to support helper classes like rule, logger, Registry, Timer, etc.
# and automatically injects `from openhab import rule, Registry, logger` into you Python code.
#
# If auto injection is disabled, the helper module can still be used by importing it manually.
#
# When completely disabled, you get a "pure" Graalpy context that has only been initialized with the default JSR223 presets.
#
# 4 => Auto injection everywhere, including script files and transformations
# 3 => Auto injection for Script Actions, Script Conditions and transformations
# 2 => Auto injection only for Script Actions & Script Conditions (recommended)
# 1 => Disable auto-injection and import manually instead
# 0 => Disable completely
#
#org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting:injectionEnabled = 2
# Python pip modules
#
# A comma separated list of Python modules to install
# Versions may be constrained by separating with an "==" followed by standard
# python pip version constraint, such as "tzdata==2025.2".
#
#org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting:pipModules =
# Enable dependency tracking
#
# Dependency tracking allows your scripts to automatically reload when one of its dependencies is updated.
# You may want to disable dependency tracking if you plan on editing or updating a shared library, but don't want all
# your scripts to reload until you can test it.
#
#org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting:dependencyTrackingEnabled = true
# Cache compiled openHAB Python modules (.pyc files)
#
# Cache the openHAB python modules for improved startup performance.<br>
# Disable this option will result in a slower startup performance, because scripts have to be recompiled on every startup.
#
#org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting:cachingEnabled = true
# Enable jython emulation
#
# This enables Jython emulation in GraalPy. It is strongly recommended to update code to GraalPy and Python 3 as the emulation can have performance degradation.
# For tips and instructions, please refer to <a href="https://www.graalvm.org/latest/reference-manual/python/Modern-Python-on-JVM">Jython Migration Guide</a>.
#
#org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting:jythonEmulation = false
# Console
The openHAB Console (opens new window) provides access to additional features of these Add-on.
pythonscripting infois showing you additional data like version numbers, activated features and used path locations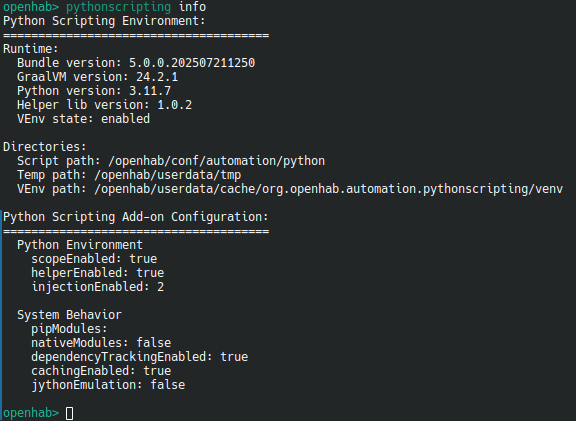
pythonscripting consoleprovides an interactive python console where you can try live python features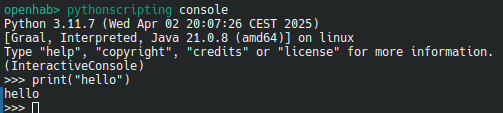
pythonscripting updateallows you to check, list, update or downgrade your helper lib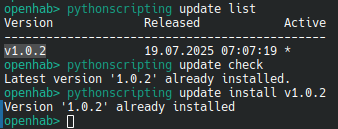
pythonscripting pipallows you check, install or remove external python modules.
Check pip usage for detailspythonscripting typinggenerates python type hint stub files.
Check python autocompletion for details
# Enabling VEnv
VEnv based python runtimes are optional, but needed to provide support for additional modules via 'pip' and for native modules. To activate this feature, simply follow the steps below.
- Login into openHAB console (opens new window) and check your current pythonscripting environment by calling
pythonscripting info
Important values are:
GraalVM version: 25.0.1VEnv path: /openhab/userdata/cache/org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting/venv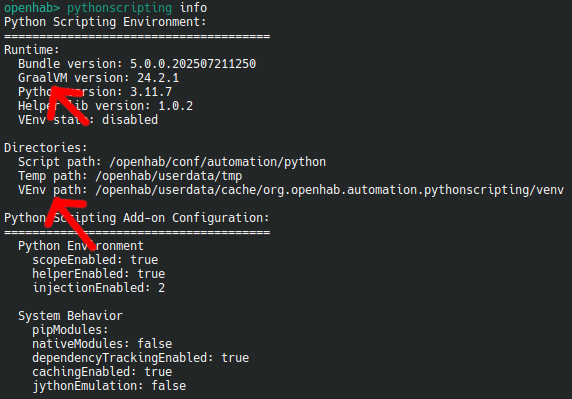
These values are needed during the next step
Download graalpy-community and create venv
Choose the correct GraalVM version
Ensure that you include the right version of your installed GraalVM in the download command. The version must match the version provided by openHAB.
# The downloaded graalpy-community tar.gz must match your operating system (linux, windows or macos), your architecture (amd64, aarch64) and your "GraalVM version" of openHAB # Exemplary code for GraalVM version 25.0.1 wget -qO- https://github.com/oracle/graalpython/releases/download/graal-25.0.1/graalpy-community-25.0.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz | gunzip | tar xvf - cd graalpy-community-25.0.1-linux-amd64/ # The venv target dir must match your "VEnv path" of openHAB ./bin/graalpy -m venv /openhab/userdata/cache/org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting/venvInstall 'patchelf' which is needed for native module support in graalpy (optional).
apt update apt-get install patchelf # zypper install patchelf # yum install patchelf
After these steps, venv setup is done and will be detected automatically during next openHAB restart.
VEnv note
Theoretically you can create venvs with a native python installation too. But it is strongly recommended to use graalpy for it. It will install a "special" version of pip in this venv, which will install patched python modules if available. This increases the compatibility of python modules with graalpython.
In container environments, you should mount the 'graalpy' folder to, because the venv is using symbolik links.
# Using pip to install external modules
As first, you must enable VEnv. After this is enabled, you can use pip in 2 ways.
Using the pythonscripting console
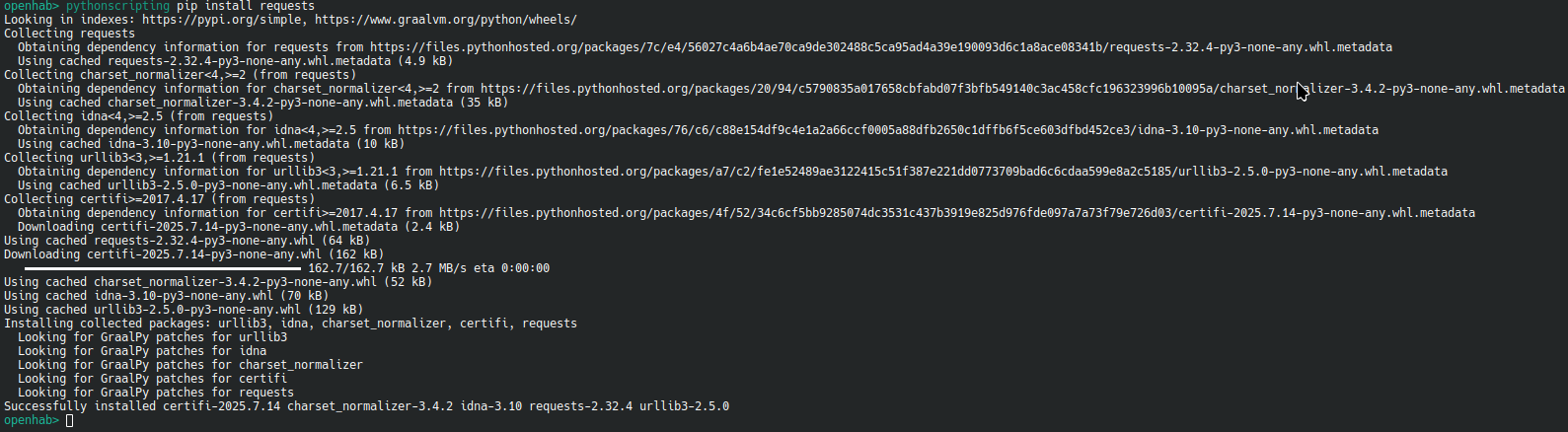
Using venv pip on your host system
/openhab/userdata/cache/org.openhab.automation.pythonscripting/venv/bin/pip install requests
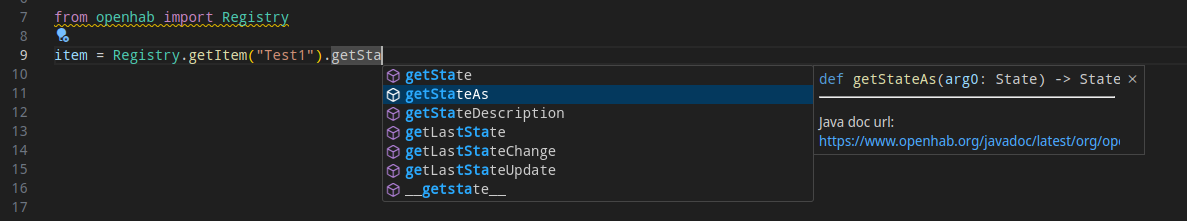
# Enable Python Autocompletion
Before you can enable autocompletion, you must generate the required type hint stub files. Login into openHAB console (opens new window) and run
pythonscripting typing
This will scan your current openHAB instance, including all installed Add-ons, for public java class methods and create corresponding python type hint stub files.
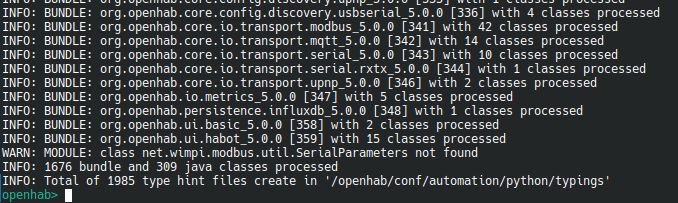
The files are stored in the folder /openhab/conf/automation/python/typings/.
As a final step, the folders /openhab/conf/automation/python/libs/ and /openhab>/conf/automation/python/typings/ must be added as "extraPaths" in your IDE.
# Typical log errors
# Graal python language not initialized. ...
2025-07-25 12:10:06.001 [ERROR] [g.internal.PythonScriptEngineFactory] - Graal python language not initialized. Restart openhab to initialize available graal languages properly.
This can happen after a new Add-on installation, if JavaScript Scripting is active at the same time.
Just restart openhab to initialize available graal languages properly.
# User timezone 'XYZ' is different than openhab regional timezone ...
2025-07-22 09:15:53.705 [WARN ] [g.internal.PythonScriptEngineFactory] - User timezone 'Europe/London' is different than openhab regional timezone 'Europe/Berlin'. Python Scripting is running with timezone 'Europe/London'.
These error happens if timezone settings are provided in several ways and some of them are different.
- Check that your EXTRA_JAVA_OPTS="-Duser.timezone=" setting is matching your openHAB regional setting.
- Additionally the ENVIRONMENT variable 'TZ', if provided, must match your openHAB regional setting.
e.g. in openHABian this can be changed in /etc/default/openhab
or for containers, this can be provided as a additional environment variable.
# Can't install pip modules. VEnv not enabled.
2025-07-22 09:19:05.759 [ERROR] [rnal.PythonScriptEngineConfiguration] - Can't install pip modules. VEnv not enabled.
You configured preinstalled pip modules, but the mandatory VEnv setup is not initialized or detected. Please confirm the correct setup, by following the steps about Enabling VEnv
# Exception during helper lib initialisation
2025-07-20 09:15:05.100 [ERROR] [rnal.PythonScriptEngineConfiguration] - Exception during helper lib initialisation
There were problems during the deployment of the helper libs. A typical error is an insufficient permission. The folder "conf/automation/python/" must be writeable by openHAB.
# Failed to inject import wrapper for engine ...
2025-07-20 10:01:17.211 [ERROR] [cripting.internal.PythonScriptEngine] - Failed to inject import wrapper for engine
The reading the Python source file "conf/automation/python/lib/openhab/__wrapper__.py" failed.
This could either a permission/owner problem or a problem during deployment of the helper libs. You should check that this file exists and it is readable by openHAB. You should also check your logs for a message related to the helper lib deployment by just grep for "helper lib".
# Limitations
- GraalPy can't handle arguments in constructors of Java objects. Means you can't instantiate a Java object in Python with a parameter. https://github.com/oracle/graalpython/issues/367 (opens new window)